Extinguish the smoldering fire inside you
Manage inflammation with a healthy lifestyle
Article Author: Beth Stambaugh
Article Date:
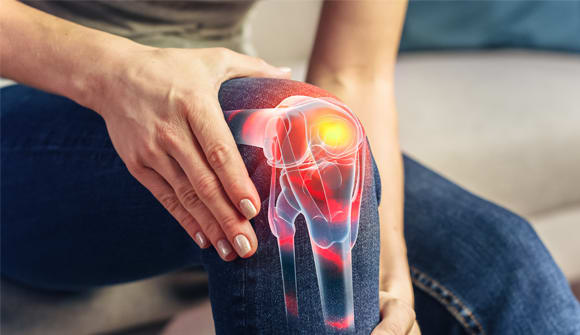
It's something you can't live without, but too much can lead to a host of chronic diseases.
Inflammation is your body's response to an infection or injury. It shows up as heat, pain, redness or swelling. It also can lead to a fever and swollen glands when you're sick. Inflammation comes to the rescue with white blood cells and platelets to help us heal.
When you're anxious or afraid, inflammation is also your body's response to help you escape a life-threatening situation. After you experience an injury or illness, inflammation is supposed to go away, but sometimes it doesn't.
Chronic inflammation and chronic diseases
"Chronic inflammation is at the root of almost every chronic disease," said Mona Shah, MD, a Baptist Heart Specialists cardiologist certified in holistic medicine. "And unfortunately, it goes unnoticed most of the time. It's like a smoldering fire building up inside our bodies."
"Over time, inflamed cells can cause blockage, rupture and damage to healthy cells and tissue," said Dr. Shah.
The list of conditions that have inflammation as a common denominator goes on and on – from heart disease to cancer, stroke and arthritis to depression, fibromyalgia, migraines and neurological diseases.
"When you consider that half of all adults have one chronic condition and that seven out of 10 patients die due to chronic diseases, it's clear that taking anti-inflammatory measures can save your life," said Dr. Shah.
Dr. Shah's mission is to educate patients on the connection between a healthy lifestyle and heart health, but her advice can help with a multitude of illnesses.
Managing inflammation through diet
Dr. Shah's No. 1 piece of advice is to eat healthy. "I don't believe in going on 'diets' because those are usually short-lived. It's more about adopting a healthy lifestyle you can live with."
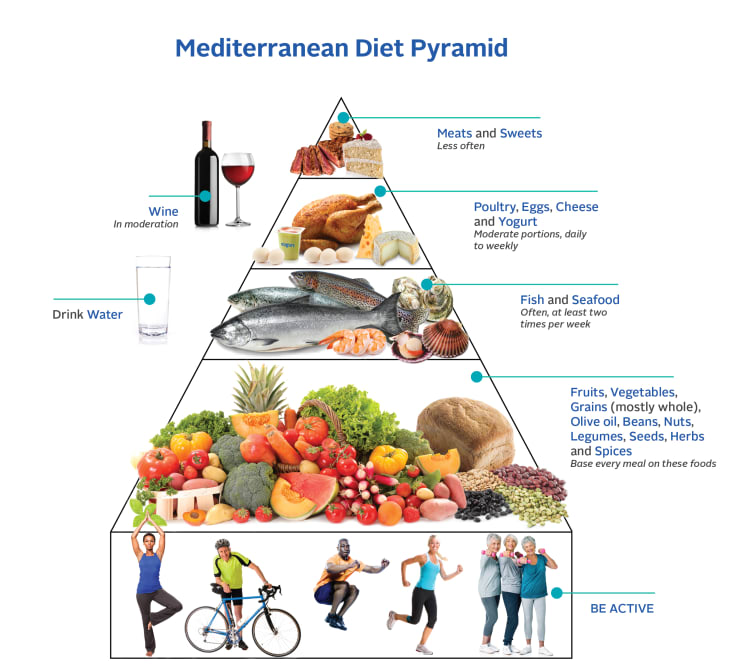
A good place to start, she said, is to follow the Mediterranean eating plan at least 80% of the time.
"The most common cause of inflammation is what you eat," she said.
Complex carbs
Dr. Shah recommended sticking to complex carbohydrates like quinoa (pronounced "keen-wa"), brown rice and sweet potatoes and limiting your intake of simple carbohydrates which include sugars and refined grains that have been stripped of fiber and nutrients. A few examples include white bread, pizza dough, pastries, white rice and many breakfast cereals.
"In general, carbohydrates convert to sugar which is why complex carbs are better," said Dr. Shah. "Always look at the food labels when shopping and the amount of added sugar. It's best to try not to consume more than 25 grams of added sugar in a day. Increased consumption of added sugars can lead to insulin resistance which is well known to increase inflammation."
Healthy fats
When it comes to fats, Dr. Shah recommended sticking to healthy fats, like avocados, nuts, seeds and olive oil and limiting your intake of saturated fats, such as cream, cheese and butter. Some saturated fats – like coconut oil, pure grass-fed butter, and even eggs – are OK in small amounts.
"You want to stay away from trans-fats, especially anything with hydrogenated oil, like vegetable, corn or soybean oil," said Dr. Shah. "Take a look at food labels and avoid anything containing partially hydrogenated vegetable oil, which causes inflammation."
Lean protein
Eat free-range and organic meats to steer clear of hormones and other chemicals. Wild fish rather than farmed is one of Dr. Shah's recommendations, as is having some vegetarian days where you stay away from animal protein altogether.
"While it's important to pay attention to the types of food you consume, remember that portion size is equally important," said Dr. Shah.
Dr. Shah has witnessed many patients who've greatly improved their health by adopting a healthier eating lifestyle. "I've seen decreases in cholesterol and blood pressure, improvements in heart health, and weight loss. The best part is that patients report feeling much better."
Anti-inflammatory supplements
There are also anti-inflammatory supplements, including magnesium, garlic, green tea, turmeric and Coenzyme Q10 (coq10), to name a few, which Dr. Shah said can be helpful for the right patient and in the right setting. Ask your doctor about the right supplement dosages for you.
Baptist Health offers the region's most comprehensive cardiovascular care
Baptist Heart Specialists offer a number of wellness and prevention programs to help patients maximize their heart-healthy lifestyle.
To learn more about eating a healthy diet to lower inflammation, read Dr. Shah's personal blog at drmonashah.wordpress.com. All information in Dr. Shah's blog represents her own content and opinions, and do not represent those of Baptist Health.




